Euro Dental Laser Dentistry
Implantation
What are dental implants?
A dental implant is an artificial tooth-root, usually casted out of titanium, a metal that is fully accepted by the human body. The implant is inserted into the jawbone in place of a missing tooth. During the healing period, natural bone cells integrate with minuscule grooves on the surface of the implant. After healing is complete, a crown, or a fixed bridge, is anchored to the implant. Dental implants may replace a single lost tooth or several missing teeth, and function just like original natural teeth do.
Advantages of implantation:
* With dental implants, remaining natural teeth are protected from failure due to shifting caused by unsupported gaps between teeth.
* With a tooth implant, a missing tooth is replaced without grinding down adjacent healthy teeth (as with conventional bridges).
* Implants offer a solution in cases where traditional treatments resort to removable dentures. With crowns and bridges anchored to the implants there is no embarrassment of false teeth slipping out, no pain or irritation of the gingival area.
* With dental implants, one can eat whatever one pleases. Implants feel and function just like natural teeth, providing great stability and ease of chewing.
* With implants, the process of jawbone atrophy is slowed. Altered facial contours may be restored to the original profile.
Dental implantation is a safe high quality alternative treatment that offers long lasting convenience and improved aesthetic appearance.
The procedure of implantation:
Dental implantation therapy consists of several steps.
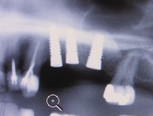
During the initial consultation at the implant centre, a dentist will assess your dental and medical health, take x-rays of your teeth, check the condition of your jawbone, and explain the recommended treatment plan along with a personalized timetable for your treatment. You’ll be able to discuss the number of implants required, the need for temporary substitutions, and the projected cost of the treatment.
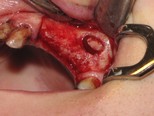
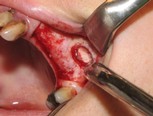
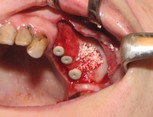
If your jawbone is found suitable for implantation, then the treatment may start even on the same day. (If your jawbone is found unsuitable as is, then it needs to be augmented preceding treatment: see the FAQ menu). The implantation procedure begins with the insertion of one or more titanium post(s) into the jawbone, along with small caps (abutments) fastened to the implants, which provide support for the future prostheses. The gum is then stitched up with absorbable stitches that dissolve naturally in a few weeks. The entire procedure is performed under local anaesthesia.
Healing period is about 3 months, during which your bone tissues integrate, and grow around the surface of the implants. The implants become stable, held firmly in place, and will tolerate the pressure of chewing and biting for a lifetime.
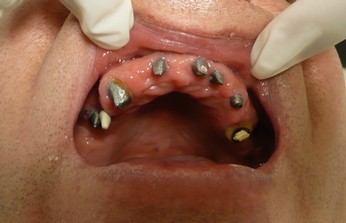
During the second visit, your dentist takes impressions of the healed gingival and your teeth for the prostheses. Your final permanent ceramic teeth will be ready in 2 to 5 days, depending on the number of crowns and bridges required. Finally, the crowns and bridges are attached to the implants.
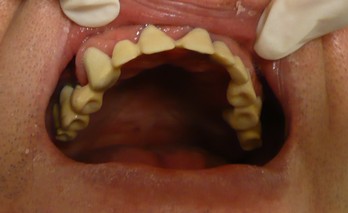
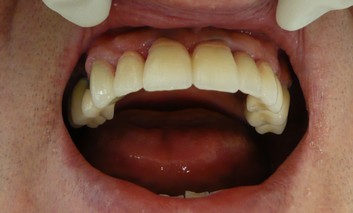
After completion of the treatment, annual dental visits to your Hungarian or local dentist are recommended, to check on the condition of your implants. If you take the same good care of your new implants as of your natural teeth, including brushing, flossing, and regular check-ups, then your implants will feel and function just like your healthy natural teeth.
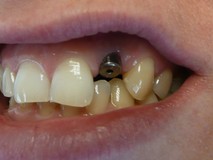
Sinus augmentation (also known as sinus lift or sinus graft) is an oral surgery procedure in which bone is added to the upper jaw,in the area of premolar and molar teeth. The goal of the surgery is to graft enough bone material onto the upper jaw to support the base of a dental implant. The procedure is performed with local anesthesia, requiring up to six months of healing for the sinus augmentation to support dental implants.
Prior to undergoing sinus augmentation, diagnostics are run to determine the health of the patient’s sinuses. Panoramic X-rays are taken to map out the patients upper jaw and sinuses. In special instances, a computed tomography or CT scan is taken to measure the sinus’s height and width, and to rule out any sinus disease or pathology.